PROJECT HIGHLIGHTS
SKILLS AND TECHNOLOGY
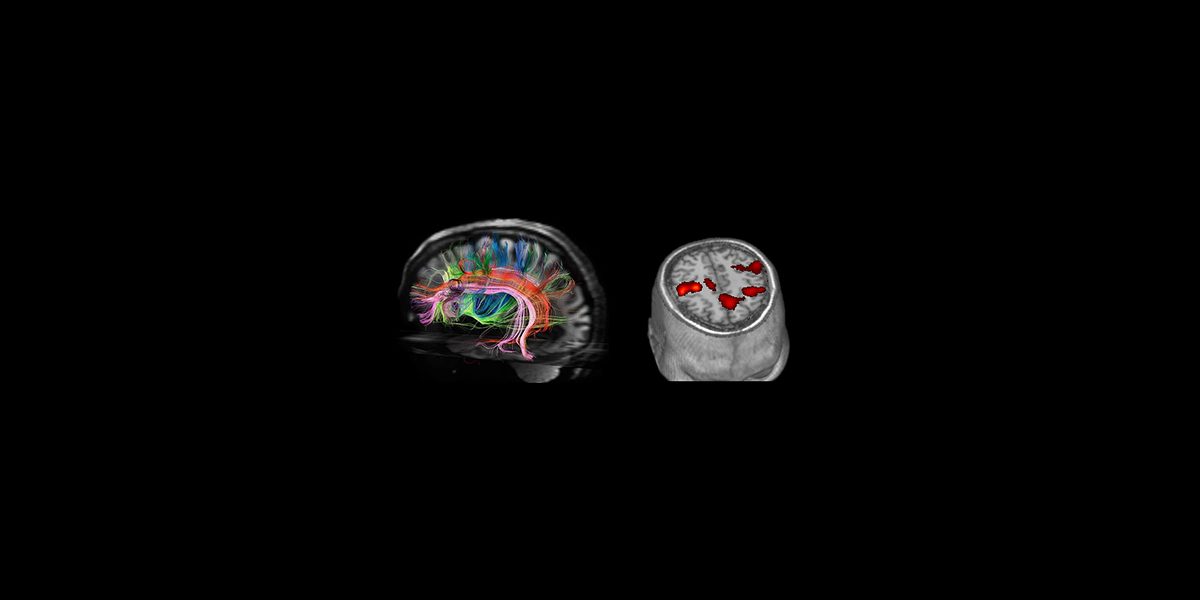
QBase will provide consultation services (Data analysis and modelling) using state of the art neuroimaging data (fMRI, DTI, 3D Volumetrics) and methods (GLM, DCM, TBSS, Graph theory, DARTEL, Surface analysis) as well as robotic device outputs, serious game score elements and clinical data. Prognostic models will be constructed using standard statistical tools (i.e. Generalized equation modelling) and machine learning approaches.
SOME DETAILS
Stroke is a major cause of morbidity and invalidity in modern society. A novel Magnetic Resonance Compatible Hand Robotic Device combined with state-of-the-art in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of brain structure and function will provide biomarkers that can be used to evaluate and predict the effects of training on the motor skills and brain recovery of stroke patients. The findings will advance stroke recovery research, which has been hampered from the longstanding view that lost functions were not recoverable and may ultimately contribute to improving the quality of life of stroke patients especially in the elderly where stroke is more prevalent.